What is a product manager?
A product manager is the person who identifies the customer need and the larger business objectives that a product or feature will fulfill, articulates what success looks like for a product, and rallies a team to turn that vision into a reality. After 10 years of studying the craft of product management, I’ve developed a deep understanding of what it means to be a product manager.
The confusion about what a product manager is likely stems from the recency of the role. Where practitioners of more established crafts, like design and engineering, have been able to segment themselves by their specialization, product managers are still defining what the role should be.
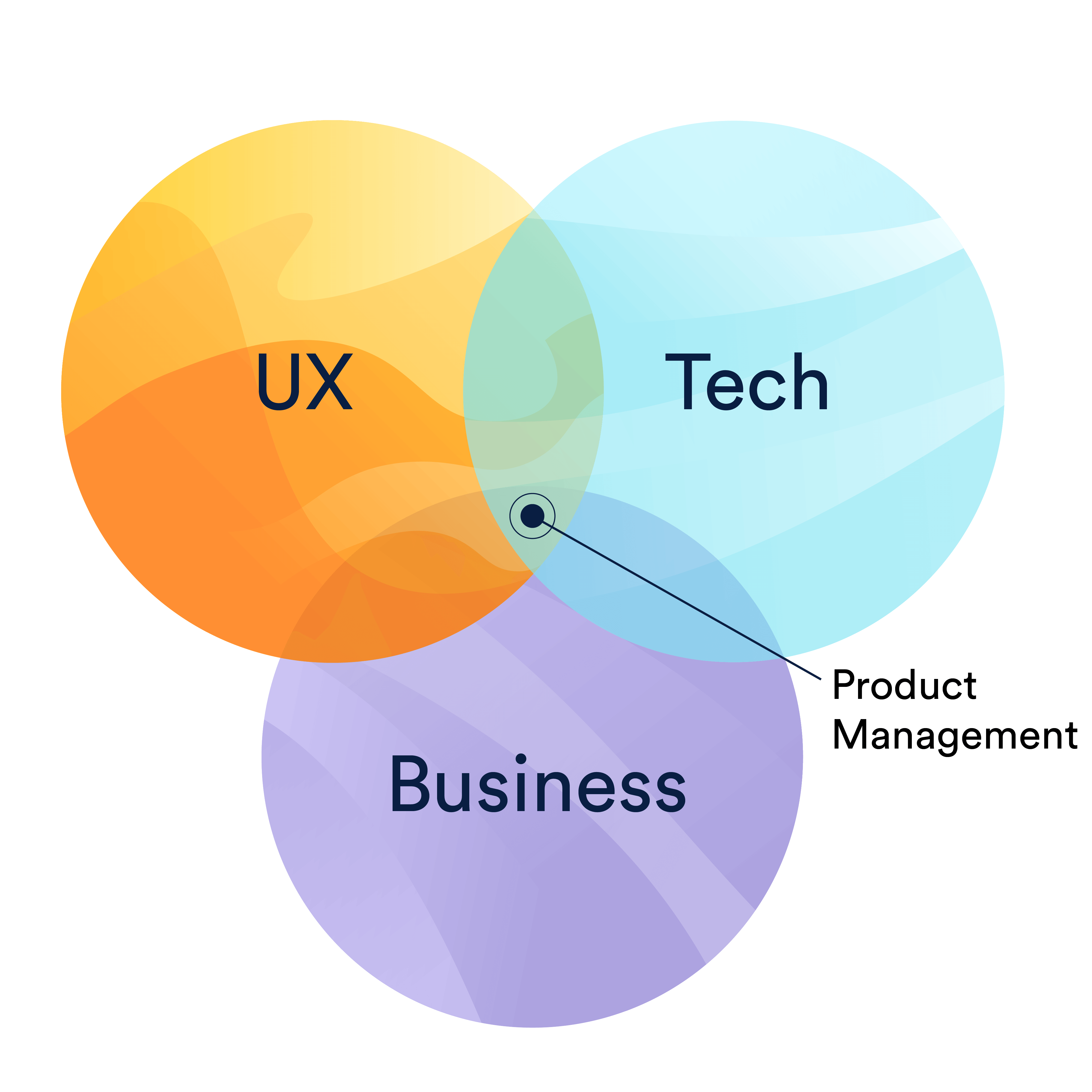
Martin Eriksson, product leader extraordinaire and founder of ProductTank, initially summed up product management in a simple Venn diagram that sits the product manager at the intersection of business, technology, and user experience. Fifteen years ago, Ben Horowitz, CEO of Opsware, called the product manager the “CEO of the product.”
I agree with both Eriksson and Horowitz, but not always with how their definitions are interpreted. People see Eriksson’s diagram and think that product managers manage the product between all three disciplines (UX, technology, and business). Really, though, he's saying product managers need to balance all three needs and make hard decisions and trade-offs. People hear Horowitz’s analogy and think product managers have some kind of special authority. They don’t. But, like a CEO, product managers set the goals, define success, help motivate teams, and are responsible for the outcome.
Product manager responsibilities
Specific responsibilities vary depending on the size of the organization. In larger organizations, for instance, product managers are embedded within teams of specialists. Researchers, analysts, and marketers help gather input, while developers and designers manage the day-to-day execution, draw up designs, test prototypes, and find bugs. These product managers have more help, but they also spend more time aligning these stakeholders behind a specific vision.
On the flip side, product managers at smaller organizations spend less time getting everyone to agree, but more time doing the hands-on work that comes with defining a vision and seeing it through.
Broadly speaking, though, a good product manager will spend his or her time on a handful of tasks.
Understanding and representing user needs.
Monitoring the market and developing competitive analyses.
Defining a vision for a product.
Aligning stakeholders around the vision for the product.
Prioritizing product features and capabilities.
Creating a shared brain across larger teams to empower independent decision-making.
Product manager vs. product owner
Whether or not a team is adhering to a certain agile practice (and which one), can further muddy the waters when it comes to what a product manager does. For instance, if a team is practicing scrum, then they also need to have a product owner.

While a product manager defines the direction of the product through research, vision-setting, alignment, and prioritization, the product owner should work more closely with the development team to execute against the goals that the product manager helps to define.
Here’s how that tends to break out:
Involved in day-to-day activities
| Product Manager | Product Owner |
|---|---|
Works with outside stakeholders | Works with internal stakeholders |
Helps to define the product vision | Helps teams execute on a shared vision |
Outlines what success looks like | Outlines the plan for achieving success |
Owns vision, marketing, ROI | Owns team backlog and fulfillment work |
Works at a conceptual level | Involded in day-to-day activities |
But responsibilities can shift a bit when team makeups and practices shift. For instance, if the team isn’t doing Scrum (say, they’re doing kanban or something else), the product manager might end up doing the prioritization for the development team and play a larger role in making sure everyone is on the same page. On the other hand, if the team is doing Scrum, but doesn’t have a product manager, then the product owner often ends up taking on some of the product manager’s responsibilities.
All of this can get really murky really quickly, which is why teams have to be careful to clearly define responsibilities, or they can risk falling into the old ways of building software, where one group writes the requirements and throws it over the fence for another group to build. When this happens expectations get misaligned, time gets wasted, and teams run the risk of creating products or features that don’t satisfy customer needs.
Best practices and tips for being a great product manager
Just as there isn’t only one kind of team, one of the most exciting aspects of the product manager role is that there isn’t only one way to do it. During the last two decades, the craft has exploded both in popularity and approach. Unlike designers who have successfully segmented themselves into interaction designers, graphic designers, motion designers, and so on, product managers, as a whole, are still wrestling with how to label their different strengths.
To complicate matters, people are only beginning to pursue product management as their intended discipline. Where older generations “fell into product management” from engineering, design, finance, or marketing, younger generations are starting their careers with product management in mind.
That said, there are a handful of skills and practices that any good product manager will need to develop.
Prioritize ruthlessly
A colleague recently likened product management to being a politician. It’s not far off. The product manager and the politician both get an allotted amount of resources. Each role requires the practitioner to make the best use of those resources to achieve a larger goal, knowing that he or she will never be able to satisfy everyone’s needs.
At any one time, the product manager might have to decide between a feature that might make one big customer happy but upset 100 smaller customers; maintaining a product’s status quo or steering it in a new direction to expand its reach and align with larger business goals; or whether to focus on the bright and shiny or the boring and important.
Clearly understanding the costs and benefits of each choice guides the product manager toward the right decision.
Know the lay of the land
Product managers need to know the lay of the land better than anyone else. They very rarely start with a clean slate. More than likely, product managers are dropped into something that already has momentum. If they start executing without taking the time to get their bearings, they’ll make bad decisions.
Good product managers pump the brakes and start by asking questions. If you’re just starting a product management job, take the first couple of months to talk to as many customers as you can. Talk to as many internal stakeholders as you can. Understand the business model. Understand the history. Understand how different people are influenced. Understand how decisions are made. Only then, can you start making a few decisions of your own.
Empower your team to make their own decisions
Product managers can’t make every decision. Believe me. I’ve tried. At the end of the day, I nearly always have unread messages. I’m often double and triple booked. And I could spend all day answering questions and never finish.
But touching every decision isn’t the product manager's job—at least it shouldn’t be. One of the keys to great product management is empowering your team to make their own decisions by creating a shared brain—or a way of making decisions and a set of criteria for escalating them. When someone asks a product manager a question about a decision they could have made themselves, nine times out of 10 it’s because that person doesn’t have enough context to make the decision themselves. Great product managers build that context.
Learn to influence without authority
I know a junior product manager that is nearly universally respected by her team even though initially many of its members would have traded her in for a more seasoned leader given the choice. How did she change their minds? She took each person on the 30-person team out for coffee and listened to them.
Influence comes in many forms. Listening to people and understanding how they’re influenced is the first part. Figuring out how to get them on board with your point of view is the second. Becoming a great storyteller—even when you don’t have any data to back up your point—will take you a long way. Some people won’t be convinced until they see you do the work. Understanding which levers to pull with which person is the key to leading without any direct authority.
Develop a thick skin
Making tradeoffs will inevitably make people unhappy. The trick is to first make the right tradeoffs, and then be able to explain why you made the decision you did. If you’re good at explaining your decision, someone can still not like it, but more often than not, they’ll respect the way you made it. And even if they don’t, great product managers figure out a way to deal with it.
Great product managers
For me, the really great product managers are one in a million. They’re the people who can do all of the above and set incredible product visions. It’s the rare breed that’s forward-thinking, highly influential, and can walk people through the rationale behind a decision and convince them—even without data. People like Steve Jobs and Elon Musk come to mind.
We idolize these people, in part, because it’s satisfying to put a face and a name on a big accomplishment. But 99 percent of the time, great products aren’t made by a single great thinker. They’re made by teams of good people doing really good work. The job of the product manager is to develop his or her unique way of guiding that work.






